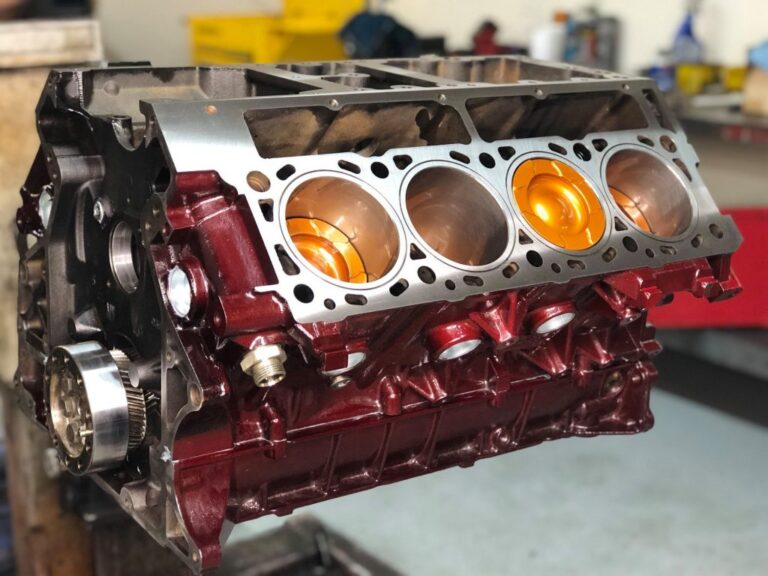
Engine blocks, the heart of any vehicle’s power system, come in various designs and materials, each suited to specific applications and performance requirements. Understanding these variations is crucial for anyone interested in automotive mechanics or considering an engine upgrade.
Materials Matter
The journey into the world of engine blocks begins with materials. Traditionally, engine blocks were made of cast iron due to its strength and durability. However, this material’s weight became a drawback, especially as fuel efficiency grew in importance.
Enter aluminum – lighter, still robust, but more prone to wear and less heat tolerant compared to cast iron. The choice between these two materials hinges on the balance between performance and durability.
Rotary Engines
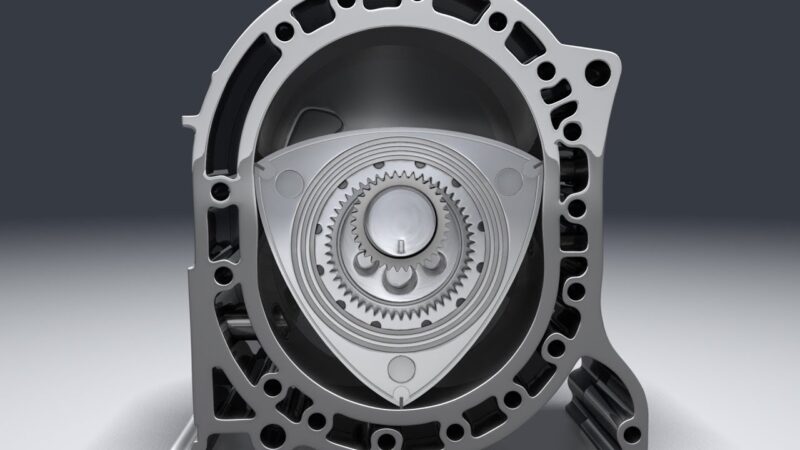

Rotary engines, a less common but fascinating type, eschew the traditional piston and cylinder design. Instead, they use a rotor that spins inside a chamber, performing intake, compression, power, and exhaust strokes in different parts of the chamber.
Renowned for their smooth operation and high power-to-weight ratio, rotary engines have been a hallmark of Mazda’s sports cars. However, their quirks, including higher fuel consumption and oil usage, have limited their widespread adoption. Learn more at monsterengineparts.com.
Inline Engines
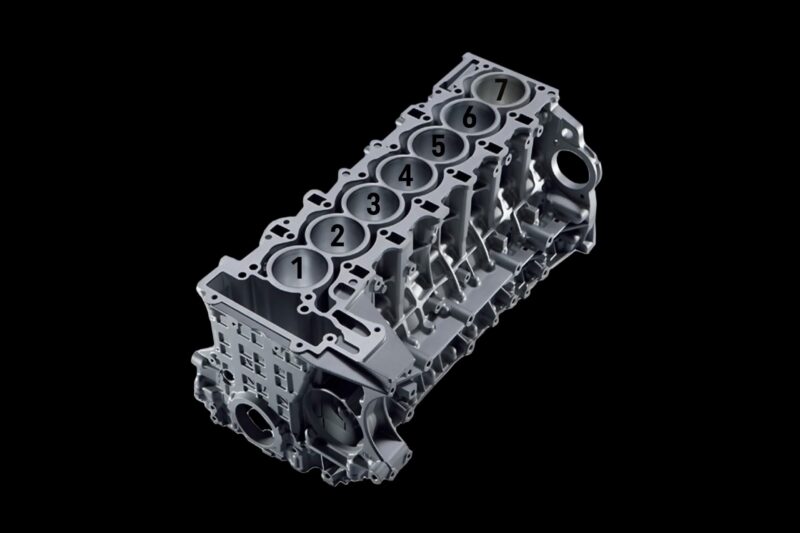

Inline engines, where cylinders are arranged in a single row, are among the most common layouts. The inline-four, a staple in compact and economical cars, offers a balance of efficiency and simplicity.
Its straightforward design translates to lower manufacturing costs and ease of maintenance. But inline engines aren’t without their limitations. The length of these engines can be a constraint in small engine bays, and their balance isn’t optimal for larger configurations.
V Engines

V engines, with cylinders arranged in two banks forming a ‘V’ shape, are synonymous with power and performance. The V6, a versatile and balanced design, finds a home in everything from sedans to sports cars.
It offers a compact design compared to an inline-six, making it suitable for a wide range of vehicles. Meanwhile, the V8 engine, often found in performance and luxury vehicles, provides even more power, making it a favorite for those seeking high performance.
Flat Engines

Flat engines, or boxer engines, feature cylinders laid out horizontally in two opposing banks. This unique design results in a lower center of gravity, benefiting handling and stability. Porsche and Subaru are prominent users of this engine type.
The flat-four, common in smaller sports cars, offers a blend of performance and efficiency, while the flat-six, seen in higher-performance vehicles, provides an enhanced power output.
Hybrid Engines
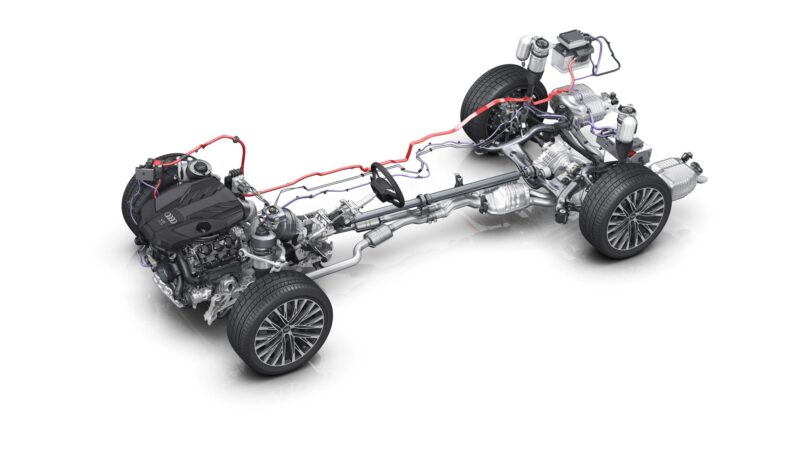
As we move towards more sustainable automotive solutions, hybrid engines are becoming increasingly relevant. These engines combine the traditional internal combustion engine with electric motors.
The synergy of these power sources offers improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. From mild hybrids that assist the combustion engine to plug-in hybrids capable of all-electric operation, this technology is at the forefront of automotive evolution.
Engine Parts
To truly appreciate the diversity of engine blocks, we must delve into the engine parts that play pivotal roles in their function. These components, integral to the performance and efficiency of any engine, deserve a spotlight.
Crankshaft
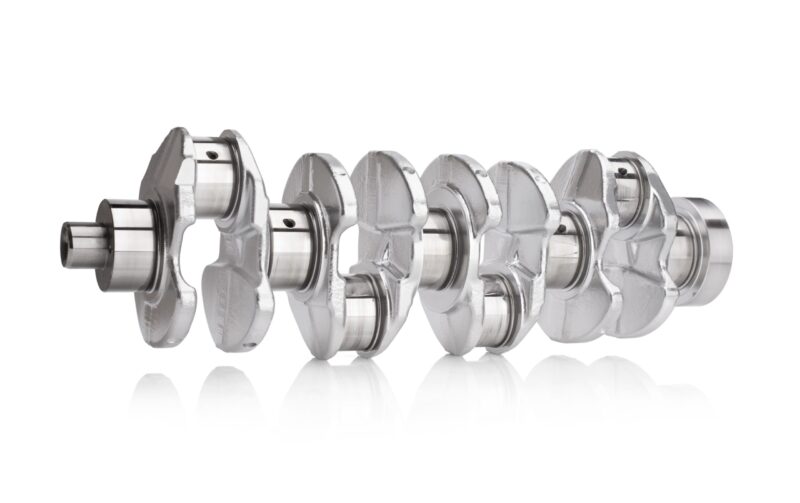

The crankshaft is the backbone of the engine, converting the linear motion of pistons into rotational motion that powers the wheels. Its design and material composition are critical for handling the immense forces generated during combustion. In high-performance engines, crankshafts need to withstand even greater stresses, demanding superior materials and construction.
Pistons
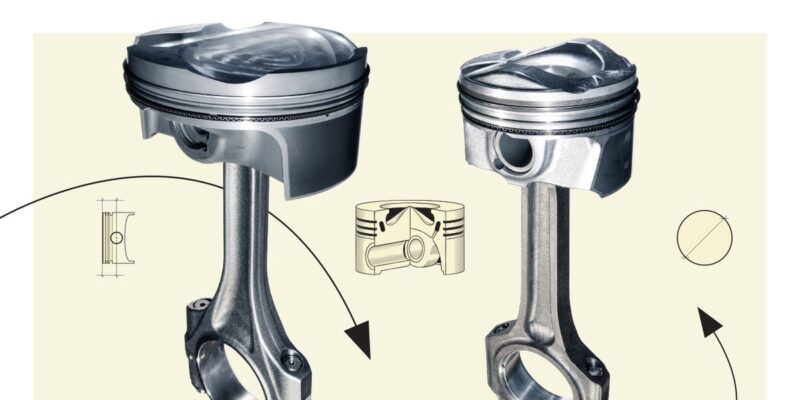
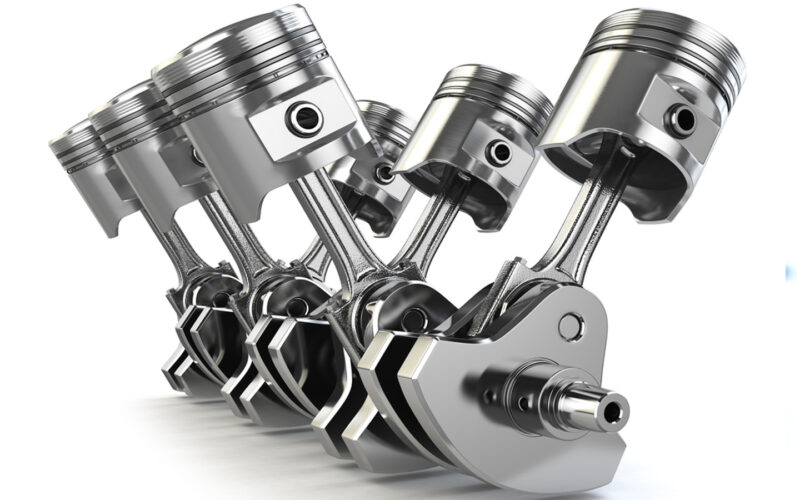
Pistons, housed within the cylinders, are the direct recipients of the combustion process’s explosive energy. They transfer this energy to the crankshaft.
The material and design of pistons vary based on the engine type and intended use. High-performance engines often use lightweight, heat-resistant materials for pistons to handle higher combustion temperatures and reduce overall engine weight.
Cylinder Heads

Cylinder heads, sitting atop the engine block, house crucial components like valves, spark plugs, and, in some engines, camshafts. They play a pivotal role in controlling airflow in and out of the engine and managing fuel delivery and exhaust.
The design of cylinder heads, especially the shape of combustion chambers and ports, greatly influences engine efficiency and performance.
Camshafts

Camshafts control the opening and closing of valves. The timing of these actions is crucial for optimal engine performance. In advanced engines, variable valve timing technology allows for dynamic adjustment of valve operation, adapting to different driving conditions for improved performance and efficiency.
Connecting Rods
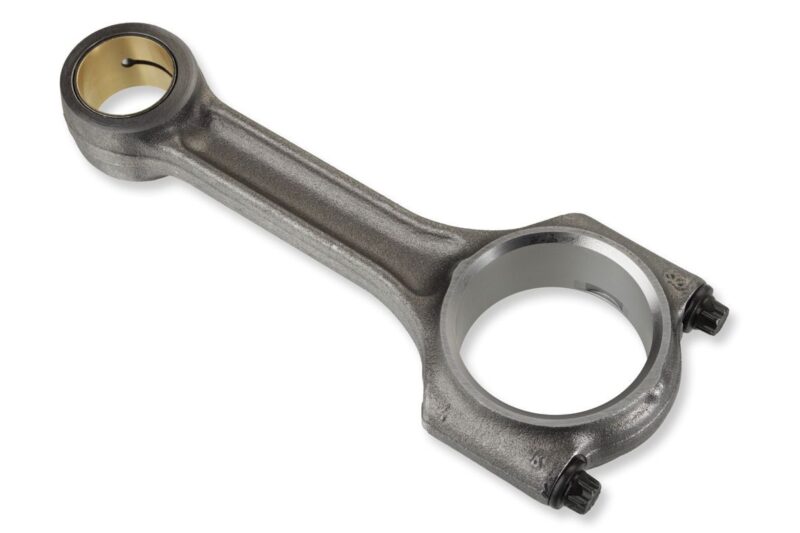

Connecting rods connect the pistons to the crankshaft, transmitting the force of the combustion process. Their design and material must balance strength and lightness to withstand high speeds and pressures while minimizing the overall engine mass.
Gaskets and Seals
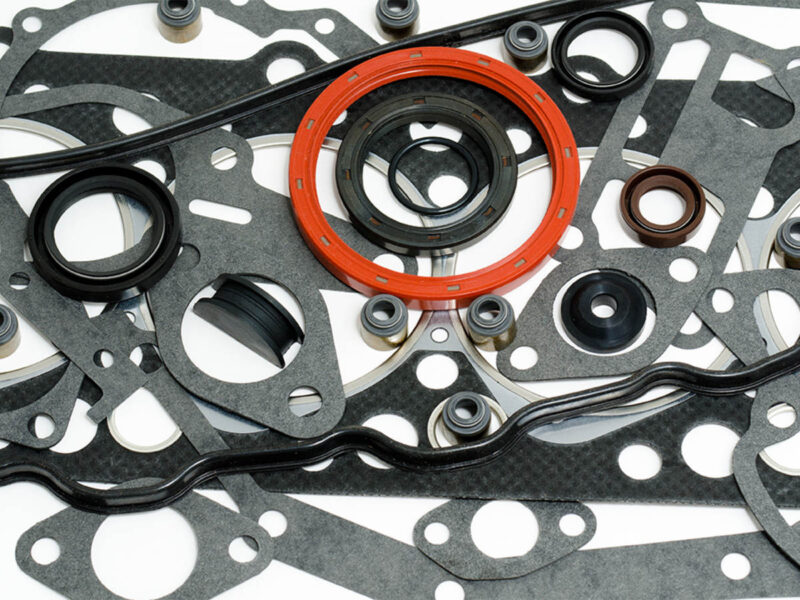

Gaskets and seals are the unsung heroes, ensuring the tightness and integrity of various engine components. They prevent oil, coolant, and fuel leaks and ensure that combustion gases are contained within the cylinders. The reliability of an engine often hinges on the quality of these components.
Engine Blocks and Beyond
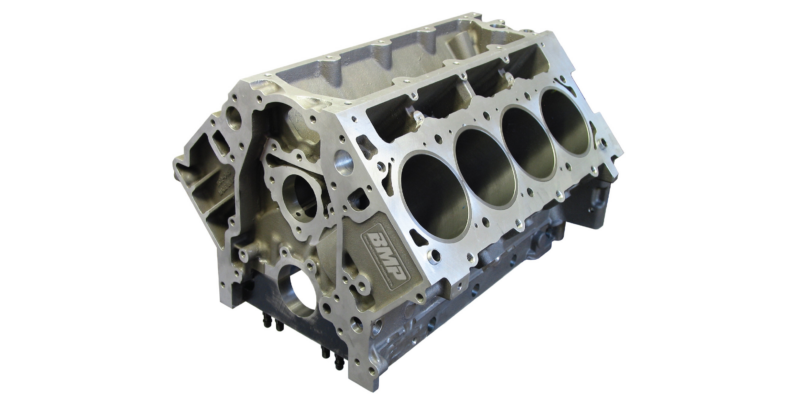
The engine block, while being the central component, works in concert with these parts to deliver the power and efficiency we expect from our vehicles. Each engine type, from the humble inline-four to the mighty V8, and the innovative hybrid systems, has its unique arrangement and specification of these parts, contributing to its distinct character and performance profile.
End Note
In conclusion, the world of engine blocks is a symphony of engineering, materials science, and mechanical artistry. Each type of engine block, with its associated components, represents a response to specific automotive needs and challenges.
From the material of the block to the design of the pistons and the timing of the camshafts, every aspect of an engine plays a crucial role in defining its character and capabilities.
As we continue to innovate and push the boundaries of automotive technology, the evolution of engine blocks and their components remains a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of improvement.
Related Posts:
- The Truth About Online Slot Manipulation: What You…
- Which Visa Do You Need to Get Married in Great…
- How to Mix Different Types of Coffee Beans Like a…
- How Long After You Create A Shipping Label Do You…
- Common Use Cases of Just-In-Time Access Explained:…
- How Accurate Is Food Sensitivity Testing? 12 Things to Know